Formerly the WRRC Brachypodium distachyon T-DNA collection.
For information about sequenced chemical and radiation mutants and other resources please visit the Brachypodium Resources site

Current collection statistics
Last Updated: 5-28-2019
- Lines in T-DNA collection: 23,649
- Unique insertions sites identified: 25,977
Project description
The small grass species Brachypodium distachyon (Brachypodium) combines the desirable attributes of a model organism with many of the traits of interest for the development and improvement of grasses (such as wheat, barley, switchgrass, and Miscanthus giganteus) that are of worldwide importance as sources of food, feed and fuel. In recognition of its utility, the DOE called for development of Brachypodium as a model plant for use in the domestication of energy crops in the 2005 report “Breaking the Biological Barriers to Cellulosic Ethanol: A Joint Research Agenda.” Since then, a comprehensive infrastructure of genomic resources has been assembled for Brachypodium.
The goal of this project (funded by the DOE Feedstock Genomics Program through interagency agreement # 60-5325-7-573) is to add to the growing collection of genomic resources available for Brachypodium by creating a large collection of T-DNA lines. These lines are indexed through flanking sequence tags (FSTs) that facilitate mapping of the T-DNA insertions within the Brachypodium genome. The collection can therefore serve to identify mutations in genes predicted to affect biomass quality and agronomic characteristics of cereal and energy crops. This paper describes the creation and sequencing of the first 8,491 T-DNA lines. This paper describes the generation and sequencing of the rest of the collection using TDNA-Seq.
- T-DNA insertions Bd21 V3 assembly 3-18-2016 (updated to the V3.o genome assembly)
- Search for insertions in specific genes using jbrowse in the Bd21 genome assembly or in the Bd21-3 genome assembly. The mutants are in line Bd21-3 but the original reference genome was made from line Bd21.
Collection details
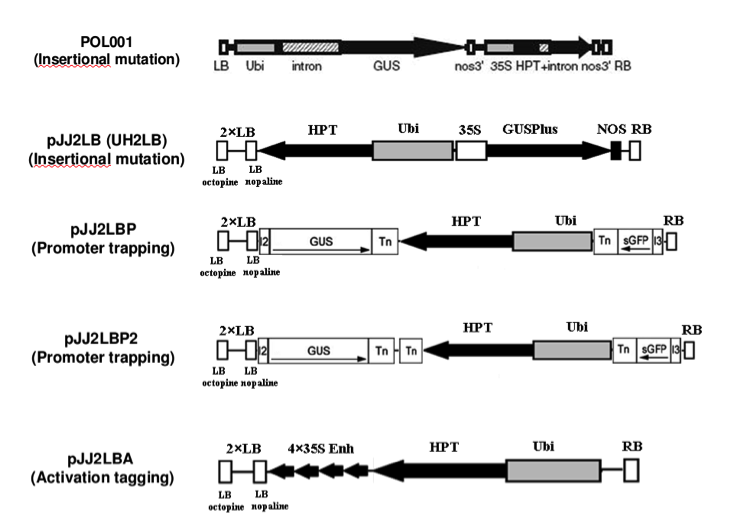
This collection comprises plants produced using a variety of constructs designed for different purposes. All lines are T-DNA insertional mutants, and therefore have the potential to create gene knockouts, and this is the exclusive purpose of lines produced using the pOL001, pJJH, pJJ2LB, pJJB, and pJJB2LB vectors. In addition, the T-DNAs of the pJJ2LBP and pJJ2LBP2 vectors contain “gene trap” sequences. In these vectors, a promotor-less GUS gene is placed adjacent to the left border, and a promotor-less GFP gene resides adjacent to the right border. If the T-DNA integrates downstream of a promoter, expression of one of the reporter genes could be used to infer the expression pattern of the disrupted gene. These constructs also contains multiple splice acceptor sites adjacent to the reporter genes to allow efficient splicing should the T-DNA fall into an intron. These lines have the potential to provide clues about the role of the disrupted gene, to provide a tool to understand the function of the disrupted gene, and to identify promoters with useful expression patterns.
The pJJ2LBA and pJJ2LBA2 vectors contain transcriptional enhancers within the T-DNA sequence. These “activation tagging” constructs are designed to increase the transcription of nearby genes. Importantly, the transcriptional enhancers are designed to give overexpression with the same expression pattern, rather than constitutive expression, of affected genes. Activation tagging is particularly well suited to assign function to genes with redundant functions where knockouts in an individual family member do not produce a phenotype.
In generating this collection, we have done an extensive evaluation of vectors built with different promoters, reporter genes, and selectable markers in order to optimize transformation efficiency. We have observed considerable variation in efficiency and plant survival and fertility depending on the construct used. Our observations include the following: Transformations employing hygromycin selection yielded consistently higher efficiency and survival over those using BASTA. The promoter driving the selectable marker greatly affects transformation efficiency (maize ubiquitin > CaMV 35S with a 5′ intron> CaMV 35S without a 5′ intron >> rice tubulin). Considering time and ease of evaluation, screening transformed tissue for GUS staining was more efficient than checking for GFP or RFP fluorescence. T-DNA vectors containing two left border sequences produce transformants that yield a higher rate of successfully recovering sequence flanking the T-DNA insertion sites. Ac/Ds and En/Spm transposons function in Brachypodium, but are lethal, possibly because they are too active.
Vector sequences:
Citations
For T-DNA mutants with flanking sequences beginning with the prefix “JJ” please cite:
For T-DNA mutants with flanking sequences beginning with the prefix “IL” please cite:
Ordering Brachypodium T-DNA lines from the JGI Brachypodium collection
Update 5-28-2019: Seed distribution is being transitioned to the USDA National Plant Germplasm System (NPGS). During this transition, we will be unable to fill new orders for seeds. Existing orders will be filled. Seeds are being shipped to NPGS now, but it may be some time before they are available for ordering. We will update this section once seeds start becoming available. You can also search NGPS at https://www.ars-grin.gov/npgs/ to check availability. Questions can be directed to: [email protected]
Note that we are still distributing seeds for sequenced chemical and radiation mutants. Please visit the Brachypodium Resources site for more information about these mutants.
Download this file for more information about how to genotype T-DNA lines.
Diagram of constructs used:
Information about constructs needed for completing a request for notification
construct pOL001
Phenotypic Designation Name: constitutive GUS expression
Identifying Line(s): ENTER THE LINES REQUESTED HERE
Construct(s): pOL001
Mode of Transformation: Agrobacterium tumefaciens, disarmed
Phenotype(s)
MG – Visual marker
MG – Hygromycin resistant
Genotype(s)
Selectable Marker
Screenable Marker
Construct components
Promoter: 35S promoter from Cauliflower mosaic caulimovirus – CaMV 35S constitutive promoter to drive expression of hygromycin phosphotransferase selectable marker
Gene: Hygromycin selectable marker from Escherichia coli – hygromycin phosphotransferase gene to confer hygromycin resistance as a selectable marker
3`UTR: nos3′ UTR from Agrobacterium tumefaciens – terminator at end of hygromycin phosphotransferase gene
Promoter: maize ubiquitin promoter from Zea mays – constitutive promoter to drive expression of GUS reporter gene
Gene: glucuronidase (GUS) reporter gene from Escherichia coli – reporter gene
3`UTR: nos3′ UTR from Agrobacterium tumefaciens – terminator at end of GUS gene
constructs pJJH and pJJ2LB
Phenotypic Designation Name: constitutive GUS expression
Identifying Line(s): ENTER THE LINES REQUESTED HERE
Construct(s): pJJH or pJJ2LB
Mode of Transformation: Agrobacterium tumefaciens, disarmed
Phenotype(s)
MG – Hygromycin resistant
Genotype(s)
Selectable marker
Screenable Marker
Construct components
Promoter: maize ubiquitin promoter from Zea mays – constitutive promoter to drive
expression of hygromycin phosphotransferase selectable marker
Gene: Hygromycin selectable marker from Escherichia coli – hygromycin phosphotransferase gene to confer hygromycin resistance as a selectable marker
Promoter: 35S promoter from Cauliflower mosaic caulimovirus – CaMV 35S constitutive promoter to drive expression of GUS reporter gene
Gene: glucuronidase (GUS) reporter gene from Escherichia coli – reporter gene
3`UTR: nos3′ UTR from Agrobacterium tumefaciens – terminator at end of GUS gene
constructs pJJB and pJJB2LB
Phenotypic Designation Name: constitutive GUS expression
Identifying Line(s): ENTER THE LINES REQUESTED HERE
Construct(s): pJJB or pJJB2LB
Mode of Transformation: Agrobacterium tumefaciens, disarmed
Phenotype(s)
MG – BASTA resistant
Genotype(s)
Selectable marker
Screenable Marker
Construct components
Promoter: maize ubiquitin promoter from Zea mays – constitutive promoter to drive
expression of phosphinothricin acetyltransferase selectable marker
Gene: BASTA selectable marker from Streptomyces hygrosopicus- phosphinothricin acetyltransferase gene to confer BASTA resistance as a selectable marker
Promoter: 35S promoter from Cauliflower mosaic caulimovirus – CaMV 35S constitutive promoter to drive expression of GUS reporter gene
Gene: glucuronidase (GUS) reporter gene from Escherichia coli – reporter gene
3`UTR: nos3′ UTR from Agrobacterium tumefaciens – terminator at end of GUS gene
construct pJJ2LBP2
Phenotypic Designation Name: promoter trapping construct
Identifying Line(s): ENTER THE LINES REQUESTED HERE
Construct(s): pJJ2LBP2
Mode of Transformation: Agrobacterium tumefaciens, disarmed
Phenotype(s)
MG – Hygromycin resistant
Genotype(s)
Selectable Marker
promoterless reporter GUS
promoterless reporter GFP
Construct components
Promoter: maize ubiquitin promoter from Zea mays – constitutive promoter to drive
expression of hygromycin phosphotransferase selectable marker
Gene: Hygromycin selectable marker from Escherichia coli – hygromycin phosphotransferase gene to confer
hygromycin resistance as a selectable marker
3`UTR: nos3′ UTR from Agrobacterium tumefaciens – terminator at end of hygromycin phosphotransferase gene
Gene: glucuronidase (GUS) reporter gene from Escherichia coli – reporter gene
3`UTR: nos3′ UTR from Agrobacterium tumefaciens – terminator at end of GUS gene
Gene: green fluorescent protein (GFP) reporter gene from Aequorea Victoria – reporter gene
3`UTR: nos3′ UTR from Agrobacterium tumefaciens – terminator at end of GFP gene
construct pJJ2LBA2
Phenotypic Designation Name: activation tagging construct
Identifying Line(s): ENTER THE LINES REQUESTED HERE
Construct(s): pJJ2LBA2
Mode of Transformation: Agrobacterium tumefaciens, disarmed
Phenotype(s)
MG – Hygromycin resistant
Genotype(s)
Selectable Marker
Enhancer element
Construct components
Promoter: maize ubiquitin promoter from Zea mays – constitutive promoter to drive
expression of hygromycin phosphotransferase selectable marker
Gene: Hygromycin selectable marker from Escherichia coli – hygromycin phosphotransferase gene to confer
hygromycin resistance as a selectable marker
3`UTR: nos3′ UTR from Agrobacterium tumefaciens – terminator at end of hygromycin phosphotransferase gene
Enhancer: 4x 35S enhancer element from Cauliflower mosaic caulimovirus – CaMV 35S
construct pJJ2LBP
Phenotypic Designation Name: promoter trapping construct
Identifying Line(s): ENTER THE LINES REQUESTED HERE
Construct(s): pJJ2LBP2
Mode of Transformation: Agrobacterium tumefaciens, disarmed
Phenotype(s)
MG – Hygromycin resistant
Genotype(s)
Selectable Marker
promoterless reporter GUS
promoterless reporter GFP
Construct components
Promoter: maize ubiquitin promoter from Zea mays – constitutive promoter to drive
expression of hygromycin phosphotransferase selectable marker
Gene: Hygromycin selectable marker from Escherichia coli – hygromycin phosphotransferase gene to confer
hygromycin resistance as a selectable marker
Gene: glucuronidase (GUS) reporter gene from Escherichia coli – reporter gene
3`UTR: nos3′ UTR from Agrobacterium tumefaciens – terminator at end of GUS gene
Gene: green fluorescent protein (GFP) reporter gene from Aequorea Victoria – reporter gene
3`UTR: nos3′ UTR from Agrobacterium tumefaciens – terminator at end of GFP gene
construct pJJ2LBA
Phenotypic Designation Name: activation tagging construct
Identifying Line(s): ENTER THE LINES REQUESTED HERE
Construct(s): pJJ2LBA2
Mode of Transformation: Agrobacterium tumefaciens, disarmed
Phenotype(s)
MG – Hygromycin resistant
Genotype(s)
Selectable Marker
Enhancer element
Construct components
Promoter: maize ubiquitin promoter from Zea mays – constitutive promoter to drive
expression of hygromycin phosphotransferase selectable marker
Gene: Hygromycin selectable marker from Escherichia coli – hygromycin phosphotransferase gene to confer
hygromycin resistance as a selectable marker
Enhancer: 4x 35S enhancer element from Cauliflower mosaic caulimovirus – CaMV 35S
For more information contact : [email protected]