How Fungi Help Trees Tolerate Drought
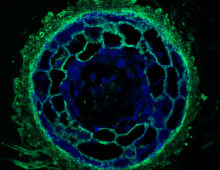
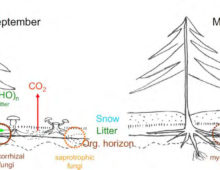
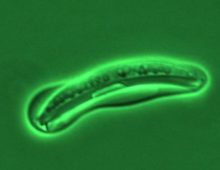
Genome of world’s most common fungal symbiont sheds light on drought resistance role The mutualistic relationship between tree roots and ectomycorrhizal (ECM) fungi has been shaping forest ecosystems since their inception. ECM fungi are key players supporting the growth, health and stress tolerance of forest trees globally, such as oak, pine, spruce, birch and beech,… [Read More]