Termite of the Sea’s Wood Destruction Strategy Revealed
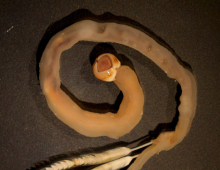
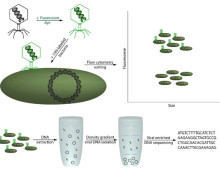
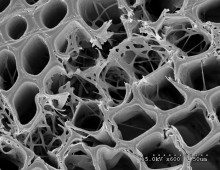
Directed production of wood-degrading enzymes begins away from the gut The sight of termites anywhere near one’s house is enough to raise a homeowner’s concerns about the potential damage these insects might inflict. Shipbuilders and engineers have similar feelings about shipworms, worm-like wood-eating marine clams that have also been called the “termites of the sea.”… [Read More]