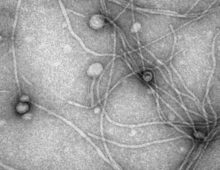
Here, There and Everywhere: Large and Giant Viruses Abound Globally
JGI-led team significantly expands the global diversity of large and giant viruses. While the microbes in a single drop of water could outnumber a small city’s population, the number of viruses in the same drop—the vast majority not harmful to humans could be even larger. Viruses infect bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes, and they range in… [Read More]