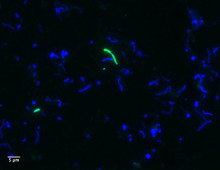
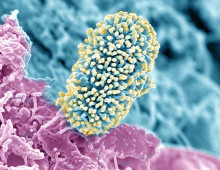
Uncovering Hidden Microbial Lineages from Hot Springs
Metagenomics and single cell strategies help reveal a novel bacterial phylum. Although global microbial populations are orders of magnitude larger than nearly any other population in, on or around the planet, only a fraction has been identified thus far. The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) is seeking to uncover the true extent of the planet’s… [Read More]