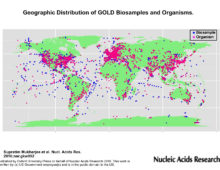
Mutant Rice Database for Bioenergy Research
Genome-wide rice studies yield first major, large-scale collection of mutations for grass models. The Science Fast-neutron irradiation, exposure to high energy neutrons, induces a wide variety of mutations by making changes in DNA. Using this approach, rice researchers were able to create the first major, large-scale collection of mutations for grass models. Resequencing the 1,504… [Read More]