Charting Short-Term Results of Wetlands Restoration
In mBio, JGI researchers reported on microbial community composition and carbon emissions patterns from restored wetlands. [Read More]
 In mBio, JGI researchers reported on microbial community composition and carbon emissions patterns from restored wetlands. [Read More]
In mBio, JGI researchers reported on microbial community composition and carbon emissions patterns from restored wetlands. [Read More]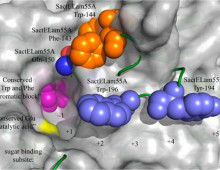 DOE-funded researchers develop a new process for annotating cellulose-degrading enzymes. The Science: Researchers at two Department of Energy-funded Scientific User Facilities collaborated with one of three Bioenergy Research Centers to develop and analyze high-resolution crystal structures of an enzyme from the cellulose-degrading GH55 family. They then went further and were able to apply a variety… [Read More]
DOE-funded researchers develop a new process for annotating cellulose-degrading enzymes. The Science: Researchers at two Department of Energy-funded Scientific User Facilities collaborated with one of three Bioenergy Research Centers to develop and analyze high-resolution crystal structures of an enzyme from the cellulose-degrading GH55 family. They then went further and were able to apply a variety… [Read More] DOE JGI researchers sequenced and analyzed a cyanobacterium with known nitrogen-fixing capabilities. The Science: Researchers sequenced and analyzed the uncommonly large genome of a nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterial strain, comparing it to the more than 150 extant cyanobacterial genomes. The Impact: Unlike many of the existing cyanobacterial genome sequences, the genome of Trichodesmium erythaeum IMS 101 is… [Read More]
DOE JGI researchers sequenced and analyzed a cyanobacterium with known nitrogen-fixing capabilities. The Science: Researchers sequenced and analyzed the uncommonly large genome of a nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterial strain, comparing it to the more than 150 extant cyanobacterial genomes. The Impact: Unlike many of the existing cyanobacterial genome sequences, the genome of Trichodesmium erythaeum IMS 101 is… [Read More] DOE JGI researchers have developed an assembly and mapping strategy for any species, including large and complex genomes. The Science: Through a combination of high-throughput sequencing, high performance computing, and genetic mapping, DOE JGI researchers have derived a sequence assembly for the highly repetitive plant genome of bread wheat (Triticum aestivum). The Impact: The researchers… [Read More]
DOE JGI researchers have developed an assembly and mapping strategy for any species, including large and complex genomes. The Science: Through a combination of high-throughput sequencing, high performance computing, and genetic mapping, DOE JGI researchers have derived a sequence assembly for the highly repetitive plant genome of bread wheat (Triticum aestivum). The Impact: The researchers… [Read More] DOE JGI is enabling collaborators to develop a universally applicable technique for studying microbial metabolic activities. The Science: A team led by University of Vienna researchers has developed a way to identify and sort single microbial cells through a probe-independent process that uses heavy water (laced with deuterium) which is then incorporated into mostly lipids… [Read More]
DOE JGI is enabling collaborators to develop a universally applicable technique for studying microbial metabolic activities. The Science: A team led by University of Vienna researchers has developed a way to identify and sort single microbial cells through a probe-independent process that uses heavy water (laced with deuterium) which is then incorporated into mostly lipids… [Read More] Researchers compared two fungal tree pathogens to find out how one of them has gained the capability to significantly damage hybrid poplar plantations. [Read More]
Researchers compared two fungal tree pathogens to find out how one of them has gained the capability to significantly damage hybrid poplar plantations. [Read More]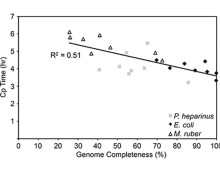 DOE JGI researchers describe the current challenges in single-cell genomics. The Science: DOE JGI researchers review the status of single-cell genomics, and how close scientists are to being able to reconstruct an individual cell’s genome. The Impact: As an alternative method of studying microbial communities, single-cell genomics allows researchers to link function to phylogeny without… [Read More]
DOE JGI researchers describe the current challenges in single-cell genomics. The Science: DOE JGI researchers review the status of single-cell genomics, and how close scientists are to being able to reconstruct an individual cell’s genome. The Impact: As an alternative method of studying microbial communities, single-cell genomics allows researchers to link function to phylogeny without… [Read More] DOE JGI, JBEI researchers collaborate on improving terpene production in E. coli. Science: Researchers from the DOE JGI and the Joint Bioenergy Institute identified genes in an E. coli microbial metabolism pathway that could improve the production of terpenes. The Impact: Terpenes are high-energy compounds produced in microbes and plants that could be used for… [Read More]
DOE JGI, JBEI researchers collaborate on improving terpene production in E. coli. Science: Researchers from the DOE JGI and the Joint Bioenergy Institute identified genes in an E. coli microbial metabolism pathway that could improve the production of terpenes. The Impact: Terpenes are high-energy compounds produced in microbes and plants that could be used for… [Read More]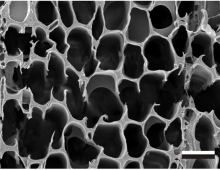 Unlike many other white rot fungi, P. gigantea prefers to colonize freshly-harvested wood. The Science: Researchers sequenced and analyzed the white rot fungus Phlebiopsis gigantea, which can break down fresh-cut conifer sapwood. They also sequenced and analyzed the set of P. gigantea’s secreted proteins (secretome) and the set of all of its RNA molecules (transcriptome)…. [Read More]
Unlike many other white rot fungi, P. gigantea prefers to colonize freshly-harvested wood. The Science: Researchers sequenced and analyzed the white rot fungus Phlebiopsis gigantea, which can break down fresh-cut conifer sapwood. They also sequenced and analyzed the set of P. gigantea’s secreted proteins (secretome) and the set of all of its RNA molecules (transcriptome)…. [Read More] Genetic maps improve the reference genome assembly of the candidate bioenergy feedstock The Science: A team of French researchers developed an array that allowed them to produce high-resolution genetic maps of two eucalyptus species that they then compared to the reference genome of eucalyptus produced by a team including DOE JGI researchers. The Impact: The… [Read More]
Genetic maps improve the reference genome assembly of the candidate bioenergy feedstock The Science: A team of French researchers developed an array that allowed them to produce high-resolution genetic maps of two eucalyptus species that they then compared to the reference genome of eucalyptus produced by a team including DOE JGI researchers. The Impact: The… [Read More]