DOE Early Career Awardee’s work to involve DOE JGI collaboration
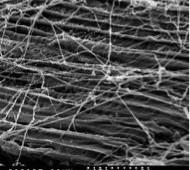
O’Malley’s research, which she recently presented at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society, involves the use of anaerobic gut fungi from horses, sheep, and other large herbivores to convert the cellulose in plants into sugars. Nature has evolved these fungi to break through lignin, a tough biopolymer that surrounds cellulose, and convert that… [Read More]