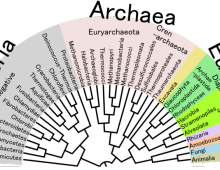
Fresh water and marine SAR11 bacteria – distant relatives and different lives
Researchers assembled genomes from several single-cell isolates of the SAR11 group of Alphaproteobacteria and found that they form microclusters within the freshwater clade. [Read More]